How Technology Shapes Swiss Type Automatic Lathe Machines
Advancements in technology have significantly influenced the manufacturing sector, particularly in precision machining. Swiss-type lathes, known for their ability to produce high-accuracy components, have undergone substantial evolution due to innovations in machine design, control systems, and tooling technologies. Understanding how these technological developments shape modern Swiss-type lathes provides insight into their enhanced efficiency, precision, and versatility.
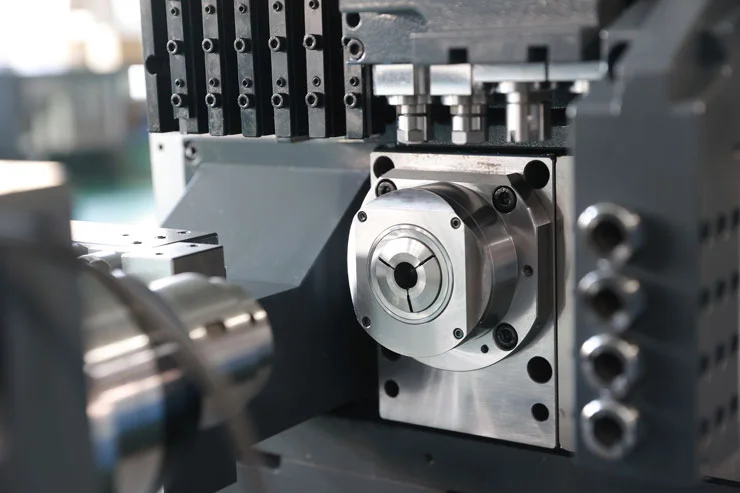
A swiss type automatic lathe machine today is far more sophisticated than its predecessors. Modern machines integrate digital controls, multi-axis capabilities, and automated systems that optimize the machining process. These improvements have expanded the range of applications for Swiss-type lathes, making them indispensable in industries such as medical devices, electronics, aerospace, and automotive components, where high precision and consistent quality are non-negotiable.
Integration of CNC Technology
One of the most significant technological advancements is the integration of Computer Numerical Control (CNC) systems. CNC technology allows operators to program complex part geometries with precision and repeatability. This level of control enables Swiss-type lathes to perform turning, drilling, milling, and threading in a single setup, reducing the need for multiple machines and setups. CNC systems also support automation features, including tool path optimization and adaptive feed rate adjustments, which enhance productivity and minimize errors.
Multi-Axis Machining Capabilities
Modern Swiss-type lathes incorporate multiple axes, which has transformed their versatility. Traditional lathes were limited to simple turning operations, but contemporary models can execute simultaneous multi-axis operations. This advancement allows for more complex component designs, including intricate geometries and micro-features, without compromising precision. The ability to perform multiple operations in one setup reduces cycle times, increases throughput, and improves overall workflow efficiency.
Advanced Tooling Technologies
Technological improvements in tooling have also shaped the evolution of Swiss-type lathes. High-performance cutting tools, coated inserts, and modular tool systems allow for extended tool life and greater cutting efficiency. These tools minimize heat generation, reduce wear, and maintain consistent dimensional accuracy, which is crucial when producing components for small-batch or high-precision applications. Moreover, live tooling capabilities allow for additional operations such as milling or drilling on rotating workpieces, further enhancing machine versatility.
Enhanced Automation and Monitoring
Automation has become a defining feature of modern Swiss-type lathes. Machines now include automatic bar feeders, tool changers, and in-process monitoring systems that reduce manual intervention. Real-time monitoring systems track spindle loads, vibration, temperature, and other parameters to detect anomalies before they affect part quality. This proactive approach to maintenance and operation ensures higher uptime, reduces scrap, and extends the life of the machine.
Precision and Stability Improvements
Technological advancements have significantly enhanced the precision and stability of Swiss-type lathes. The guide bushing system, which supports the workpiece close to the cutting tool, has benefited from improved materials and design, reducing vibration and deflection. Advanced servo motors, high-resolution encoders, and refined control algorithms contribute to tighter tolerances and superior surface finishes. These improvements are particularly valuable in industries where even minor deviations can compromise functionality or safety.
Software and Simulation Capabilities
Modern Swiss-type lathes are supported by sophisticated software platforms that facilitate simulation, programming, and process optimization. Virtual machining simulations allow operators to verify tool paths, anticipate potential collisions, and adjust parameters before actual production. This technology reduces trial-and-error cycles, minimizes waste, and ensures consistent quality across different production runs. Additionally, integrated software simplifies maintenance scheduling and resource planning, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Impact on Small-Batch and Custom Production
The integration of these technological advancements makes Swiss-type lathes particularly effective in small-batch and custom production. The combination of CNC control, multi-axis machining, advanced tooling, and automation allows manufacturers to produce highly precise components with minimal setup time. This flexibility is essential in industries where product variation is frequent, and high-quality output is required consistently.
Conclusion
Technology has profoundly shaped Swiss-type automatic lathe machines, enhancing their precision, versatility, and efficiency. CNC integration, multi-axis capabilities, advanced tooling, and automation collectively contribute to improved workflow, reduced production time, and superior part quality. Modern software and monitoring systems further ensure reliability and consistent performance. As technological innovation continues, Swiss-type lathes will remain at the forefront of precision manufacturing, enabling industries to meet increasingly complex demands with efficiency and accuracy.