Differences Between PU Foam Sealant and Other Sealants
When it comes to sealing gaps, cracks, and cavities in buildings, choosing the right sealant is essential for achieving optimal performance and durability. Among the many options available, PU foam sealant stands out due to its unique properties and versatility. Understanding how it differs from other commonly used sealants can help homeowners, contractors, and DIY enthusiasts make informed decisions for their projects.
What is PU Foam Sealant?
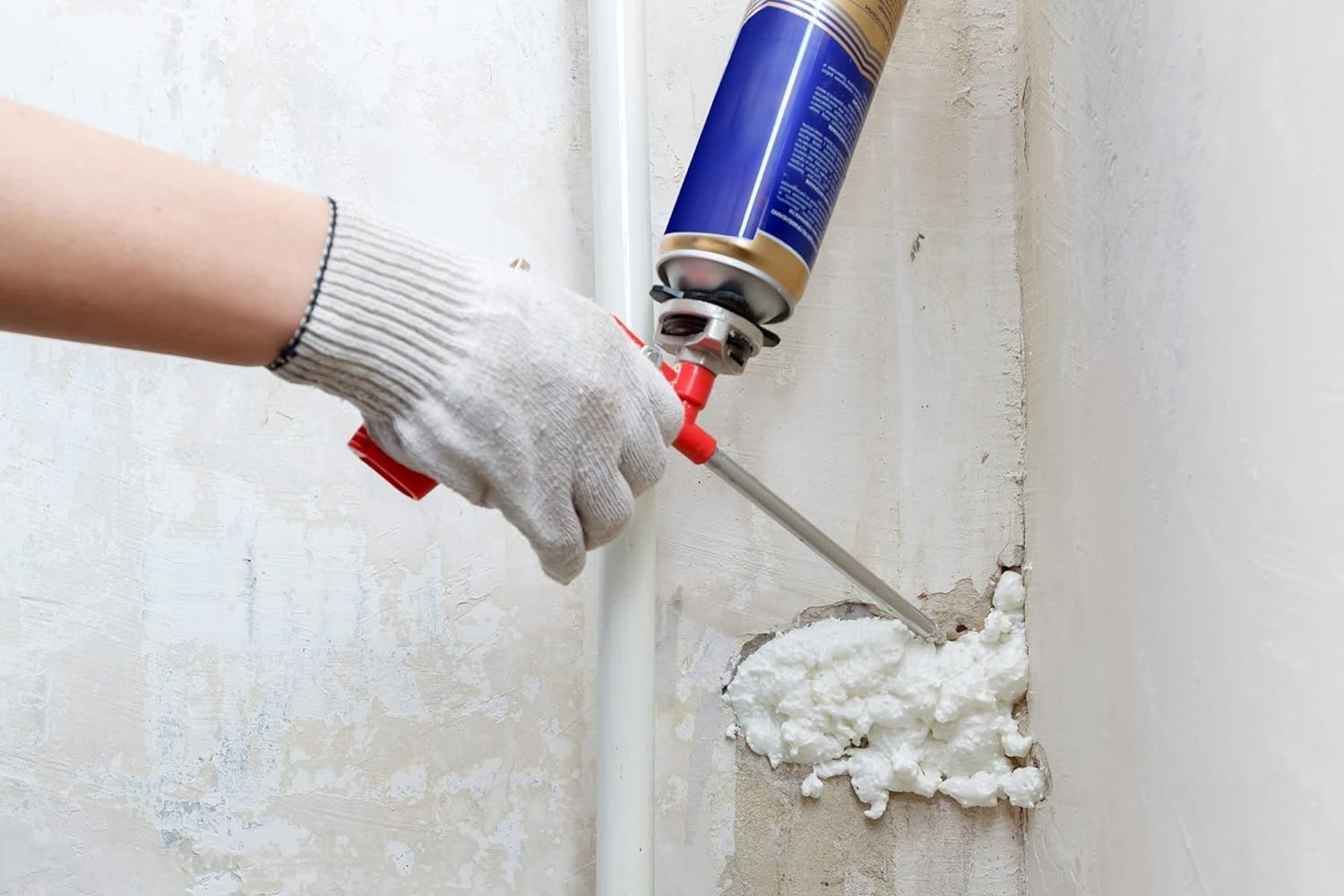
PU foam sealant is a polyurethane-based product that expands upon application to fill gaps and form a durable, airtight, and moisture-resistant seal. Unlike traditional sealants, PU foam not only seals but also provides insulation and structural support. For those looking for reliable options, PU foam sealant comes in a range of formulations tailored for specific applications, including window and door sealing, wall insulation, and pipe penetrations. Its expanding nature allows it to reach spaces that other sealants may struggle to fill effectively.
Key Differences Between PU Foam Sealant and Other Sealants
1. Expansion Properties
One of the primary differences between PU foam sealant and other types of sealants, such as silicone or acrylic, is its ability to expand. PU foam increases in volume after application, allowing it to fill irregular cavities and deep gaps efficiently. Traditional sealants typically remain in the form they are applied, which may leave voids or require multiple applications to achieve full coverage.
2. Insulation Capabilities
While most sealants are designed solely to block air or water leaks, PU foam sealant provides thermal and acoustic insulation. Its closed-cell structure reduces heat transfer and dampens sound, making it ideal for energy efficiency and noise reduction. Silicone and acrylic sealants offer minimal insulation, primarily focusing on waterproofing and flexibility.
3. Adhesion and Surface Compatibility
PU foam sealant adheres well to a wide variety of materials, including wood, metal, brick, concrete, and plastic. This versatility allows it to be used in multiple applications across construction and home improvement projects. In contrast, some sealants, such as silicone, may not bond effectively to certain porous surfaces, requiring primers or surface preparation for reliable adhesion.
4. Curing Time and Handling
PU foam sealant undergoes a chemical reaction that causes it to expand and cure into a solid, resilient foam. Depending on the product, curing times can vary from a few hours to 24 hours. Silicone and acrylic sealants typically cure on the surface first, forming a skin while remaining soft underneath for longer periods. This difference in curing behavior affects how the product can be handled, trimmed, or painted after application.
5. Moisture and Air Resistance
PU foam sealant provides excellent resistance against both air and moisture infiltration. It creates an airtight and water-resistant barrier, making it ideal for areas exposed to drafts, rain, or condensation. While silicone sealants excel at waterproofing, they are less effective in insulating and filling large gaps, and acrylic sealants may be more prone to shrinkage over time.
6. Structural Support
Because of its rigid, expanding nature, PU foam sealant can provide a degree of structural support in addition to sealing. It can help stabilize window and door frames, reduce vibration in pipes, and strengthen wall cavities. Most other sealants are flexible and designed to accommodate movement rather than provide support.
Common Applications
PU foam sealant can be used in a wide variety of applications where both sealing and insulation are required:
- Window and Door Installation: Filling gaps and providing thermal and acoustic insulation.
- Wall and Roof Cavities: Sealing and insulating structural spaces.
- Pipe Penetrations and Ducts: Preventing air leaks and reducing vibrations.
- Basements and Attics: Controlling moisture and improving energy efficiency.
Other sealants, such as silicone, are typically better suited for applications requiring flexibility, such as bathroom and kitchen joints, or acrylic for decorative caulking and paintable areas.
Conclusion
The differences between PU foam sealant and other sealants lie in expansion properties, insulation capabilities, adhesion, curing behavior, moisture resistance, and structural support. While traditional sealants like silicone and acrylic serve specific purposes, PU foam offers a combination of sealing, insulating, and supporting benefits that make it highly versatile for a wide range of home and commercial projects. Understanding these distinctions allows users to select the most appropriate sealant for each task, ensuring long-lasting performance, energy efficiency, and structural integrity.