Benefits of Using a Water pH Sensor for Continuous Monitoring
Maintaining water quality is a critical responsibility for municipalities, industries, and private water users. Consistent monitoring ensures that water remains safe for consumption, industrial processes, and environmental management. Among the key parameters for assessing water quality, pH plays a vital role. It determines whether water is acidic, neutral, or alkaline and affects taste, infrastructure, treatment efficiency, and health safety. To manage these factors effectively, continuous monitoring has become a standard practice in modern water management systems.
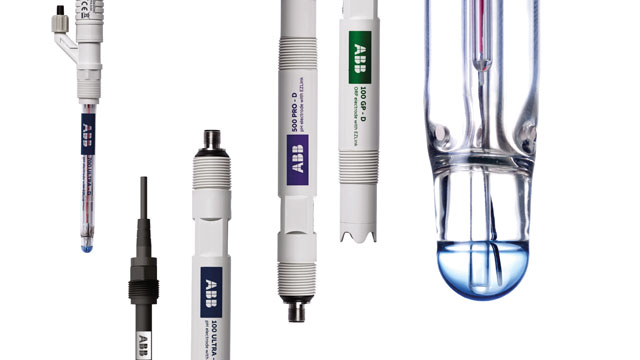
One of the most efficient tools for achieving ongoing monitoring is a water ph sensor. By providing real-time data on water’s acidity or alkalinity, this device allows operators to respond quickly to fluctuations, maintain regulatory compliance, and ensure optimal water quality. Its integration into water systems has transformed monitoring from periodic sampling into a continuous, data-driven process.
Understanding pH and Its Importance
pH measures the concentration of hydrogen ions in water, with values ranging from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is neutral, below 7 is acidic, and above 7 is alkaline. Drinking water is generally recommended to maintain a pH between 6.5 and 8.5. Water outside this range can become corrosive, reduce the efficiency of disinfection, or cause scaling in pipes and infrastructure.
Regular monitoring of pH is critical because even small deviations can create long-term problems. Continuous data from a water pH sensor allows operators to detect trends and address changes before they impact water safety, infrastructure, or treatment effectiveness.
How Continuous Monitoring Works
A water pH sensor detects the activity of hydrogen ions in water and converts this information into an electrical signal representing the pH value. Modern sensors are designed to provide accurate, stable, and rapid measurements in real time. Unlike manual testing, which offers occasional snapshots, continuous monitoring ensures that operators have a complete picture of water conditions at all times.
These sensors can be integrated into automated monitoring systems that track trends, generate alerts when pH values drift outside acceptable ranges, and support data-driven decision-making. This ensures that water management is proactive rather than reactive.
Protecting Health and Infrastructure
Maintaining the correct pH level is essential for public health. Acidic water can corrode pipes, releasing metals such as lead or copper into the water supply. Alkaline water, while less corrosive, can reduce the effectiveness of disinfectants and create scaling that affects equipment and infrastructure. Continuous monitoring using a water pH sensor allows early detection of unsafe conditions and facilitates timely interventions to prevent contamination or damage.
This proactive approach protects consumers, reduces maintenance costs, and ensures compliance with health standards. Facilities that rely on continuous pH data can avoid costly repairs and improve overall system reliability.
Optimizing Water Treatment Processes
Water treatment relies heavily on chemical processes that are sensitive to pH levels. Disinfectants, coagulants, and other treatment chemicals function most effectively within specific pH ranges. If the water is outside this range, treatment efficiency decreases, and additional chemicals may be required.
By providing accurate, real-time readings, a water pH sensor helps treatment operators adjust chemical dosing precisely. This not only ensures effective treatment but also reduces chemical waste and operational costs. Continuous monitoring is therefore both a safety measure and an efficiency booster.
Applications Beyond Drinking Water
While municipal water systems are the primary users, pH sensors are valuable in industrial, agricultural, and environmental contexts. Industries such as food processing, pharmaceuticals, and beverage production rely on precise pH control for product quality and compliance. In agriculture, monitoring irrigation water helps maintain soil health and crop yields. Aquaculture facilities depend on stable pH to maintain a healthy environment for fish and other aquatic organisms.
Across all these applications, continuous pH monitoring enables operators to maintain optimal water conditions, reduce risks, and meet regulatory standards.
Supporting Compliance and Transparency
Regulatory agencies require ongoing documentation of water quality, including pH levels. A water pH sensor facilitates compliance by providing consistent, verifiable data that can be automatically logged. This reduces the risk of human error in manual testing and ensures a clear record for audits and inspections.
Beyond regulatory compliance, continuous monitoring builds trust among consumers and stakeholders. Knowing that water quality is constantly tracked and maintained increases confidence in the safety and reliability of water systems.
Conclusion
Continuous monitoring of water quality is essential for health, efficiency, and compliance. A water pH sensor provides accurate, real-time data that supports early detection of changes, optimizes treatment processes, and protects infrastructure. By integrating these sensors into monitoring systems, water managers can maintain safe and reliable water, reduce operational costs, and meet regulatory standards consistently. This technology is indispensable for modern water quality management.