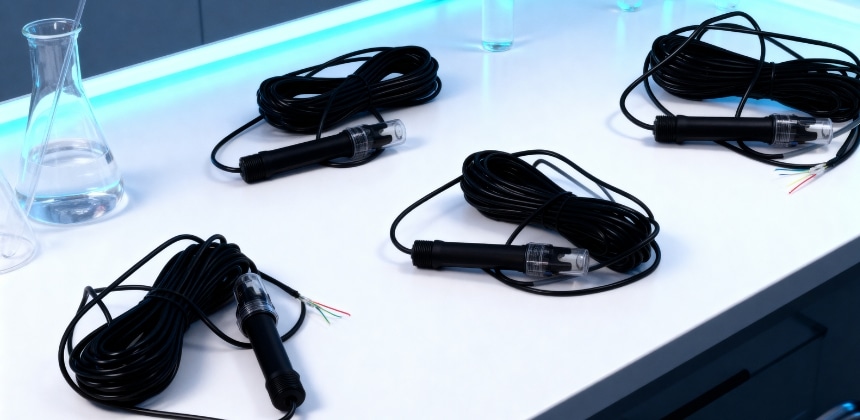
The Role of a pH Sensor in Laboratory Testing
Laboratory testing depends on accuracy, consistency, and repeatability. Whether the work involves chemical research, pharmaceutical development, food analysis, or environmental studies, precise measurement of solution properties is essential. Among these properties, pH is one of the most influential because it directly affects chemical reactions, sample stability, and analytical outcomes. Without reliable pH control, even well-designed experiments can produce misleading or unusable results.
In modern laboratories, a pH sensor is used as a core analytical tool to determine acidity and alkalinity with precision. By converting chemical activity into measurable electrical signals, this instrument allows researchers to monitor conditions in real time and maintain strict control over testing environments. Its role goes far beyond simple measurement, supporting accuracy at every stage of laboratory work.
Why pH Control Is Critical in Laboratory Experiments
Many laboratory reactions are highly sensitive to pH changes. Reaction rates, equilibrium states, and compound solubility often depend on maintaining a narrow pH range. Even slight deviations can alter outcomes, leading to inconsistent data or failed experiments.
In biochemical and pharmaceutical laboratories, enzymes and active compounds may lose effectiveness if pH conditions drift outside acceptable limits. Accurate pH measurement ensures that experimental conditions remain stable, supporting reliable and reproducible results across multiple tests and batches.
Supporting Accuracy in Analytical Techniques
Laboratory testing frequently involves analytical methods such as titration, spectroscopy, and chromatography. These techniques often rely on specific pH conditions to function correctly. For example, titration endpoints are directly related to pH changes, while chromatographic separation can be influenced by buffer acidity.
A dependable pH measurement tool helps analysts detect subtle changes that could affect test accuracy. This level of control improves confidence in results and reduces the risk of measurement errors that could compromise conclusions or require costly retesting.
Consistency in Sample Preparation
Sample preparation is a critical step in laboratory testing, and pH plays a major role in this process. Buffers, reagents, and solutions must often be adjusted to precise pH values before use. Inconsistent preparation can introduce variability that affects downstream analysis.
By enabling precise adjustment and verification of pH levels, sensors help standardize preparation procedures. This consistency ensures that samples behave predictably during testing, improving comparability between experiments and across different laboratory teams.
Applications Across Different Laboratory Fields
The importance of pH measurement spans a wide range of laboratory disciplines. In chemical research, pH affects reaction pathways and product formation. In pharmaceutical testing, it influences drug stability, solubility, and absorption characteristics. In food and beverage laboratories, pH analysis supports quality control, safety testing, and shelf-life evaluation.
Environmental laboratories also rely heavily on pH data when analyzing water, soil, and wastewater samples. Accurate measurement helps identify pollution sources, assess regulatory compliance, and evaluate environmental health. Across these fields, precise pH monitoring supports informed decision-making and scientific integrity.
Calibration and Quality Assurance in the Laboratory
Maintaining accuracy in laboratory testing requires regular calibration of measuring instruments. pH measurement is no exception. Calibration against standard buffer solutions ensures that readings remain aligned with known reference points.
Routine calibration supports quality assurance programs and helps laboratories meet accreditation and regulatory requirements. Consistent pH data also improves traceability, allowing results to be validated and audited when necessary.
Reducing Errors and Improving Efficiency
Inaccurate pH readings can lead to repeated experiments, wasted reagents, and lost time. By providing dependable measurements, pH monitoring tools reduce the likelihood of such inefficiencies. Researchers can focus on analysis and interpretation rather than troubleshooting preventable errors.
Efficient pH control also supports automation in modern laboratories. Many testing systems integrate pH measurement into automated workflows, improving throughput while maintaining high standards of accuracy.
Building Confidence in Laboratory Results
Ultimately, the role of pH measurement in laboratory testing is about building trust in data. Reliable results form the foundation of scientific progress, product development, and regulatory compliance. When pH conditions are accurately monitored and controlled, laboratories can produce data that is consistent, defensible, and meaningful.
By understanding and prioritizing the role of pH measurement, laboratory professionals strengthen the reliability of their testing processes. This commitment to precision supports better research outcomes, higher-quality products, and greater confidence in scientific conclusions.