The Role of pH Sensors in Water Quality Monitoring
Maintaining high water quality is a critical priority for public health, industrial operations, and environmental protection. Among the many parameters used to assess water quality, pH is one of the most important. It measures the level of acidity or alkalinity in water, which can directly impact aquatic life, infrastructure, and overall safety. Accurate measurement of pH is essential, and this is where pH sensors become a vital component of water monitoring systems.
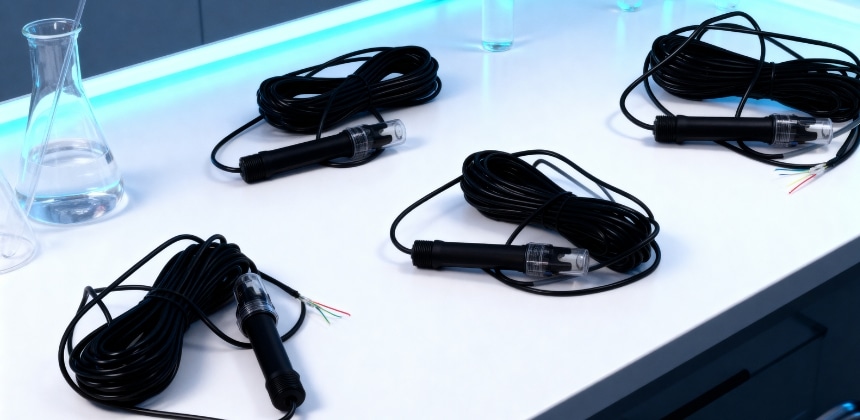
pH sensors detect the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution and convert this information into a readable electrical signal. These devices allow for precise, real-time monitoring of water, enabling operators to make timely adjustments when necessary. For a detailed overview of how these devices function and their applications, you can refer to this informative resource on pH sensors, which explains their working principles and key components.
Types of pH Sensors Used in Water Monitoring
Different applications require different types of pH sensors. Common varieties include:
- Glass Electrode Sensors: The most widely used type due to their high accuracy and versatility in measuring various water types, including freshwater, wastewater, and industrial water.
- ISFET Sensors (Ion-Selective Field Effect Transistors): Solid-state sensors offering fast response times, durability, and suitability for automated systems.
- Combination Electrodes: These integrate both the measuring and reference electrodes in a single unit, simplifying installation and maintenance while providing reliable readings.
Selecting the right sensor depends on the water composition, temperature, and presence of impurities that may affect measurement accuracy. Proper sensor choice is crucial to ensure reliable and consistent data.
Importance of Monitoring Water pH
Water pH levels are critical for multiple reasons. In drinking water systems, maintaining the appropriate pH prevents corrosion of pipes, ensures taste quality, and inhibits the growth of harmful microorganisms. In industrial operations, pH monitoring helps prevent damage to equipment caused by scaling or corrosion, ensures proper chemical reactions, and maintains compliance with environmental regulations. For natural ecosystems, pH plays a key role in supporting aquatic life and preserving biodiversity.
Calibration and Maintenance
To ensure consistent performance, pH sensors must be regularly calibrated. Calibration involves using buffer solutions with known pH values to correct any drift caused by electrode aging, fouling, or temperature changes. Maintenance routines include cleaning electrodes, checking reference solutions, and replacing parts as necessary. Regular upkeep not only ensures accurate measurements but also extends the lifespan of the sensors, making them a cost-effective solution for long-term water monitoring.
Applications in Water Quality Management
pH sensors are widely applied in water quality monitoring across various sectors:
- Drinking Water Treatment: Ensuring the water supplied to communities is safe and meets regulatory standards.
- Wastewater Management: Monitoring pH levels in effluent to prevent environmental contamination.
- Aquaculture: Maintaining optimal pH conditions to promote healthy growth of fish and other aquatic organisms.
- Industrial Water Systems: Controlling pH in cooling towers, boilers, and chemical processes to prevent damage and maintain efficiency.
Real-time data from pH sensors enables operators to take immediate corrective actions, reducing risks to human health, equipment, and the environment.
Advantages of Using pH Sensors
The use of pH sensors provides multiple benefits in water monitoring:
- Accuracy and Consistency: Sensors deliver precise readings, reducing errors associated with manual testing.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Immediate feedback allows for prompt adjustments to maintain water quality.
- Automation Compatibility: Sensors can integrate with automated control systems for continuous monitoring.
- Durability: Designed to withstand harsh water environments and long-term use.
These advantages make pH sensors an essential tool for water quality management, improving efficiency, safety, and regulatory compliance.
Conclusion
pH sensors play a crucial role in ensuring water quality for public, industrial, and environmental applications. By providing accurate and real-time data, they help prevent contamination, protect infrastructure, and support aquatic ecosystems. Regular calibration and proper sensor selection enhance reliability, ensuring that water monitoring systems operate efficiently and effectively. Incorporating pH sensors into water quality management strategies enables proactive decision-making, safeguarding both human health and the environment.